In the past year, despite the global impact of the COVID-19 epidemic, China’s science and technology have flourished. Recently, the top ten scientific advances in China in 2021 were officially released, and this post will reveal them for you.
1. The Tianwen-1 probe of the Mars exploration mission successfully landed on Mars
At 7:18 on May 15, 2021, Tianwen-1 successfully landed on Mars using the “aerodynamic deceleration – parachute deceleration – power deceleration – landing buffer” four-stage series deceleration technology route, taking an important step in my country’s interstellar exploration journey , realizing the leap from the Earth-Moon system to the interplanetary system, which is another milestone in the development of my country’s aerospace industry.
2. Tianhe core module of Chinese space station successfully launched
The Shenzhou 12th and 13th manned spacecraft were successfully launched and successfully docked with the Tianhe core module
On April 29, 2021, the Tianhe core module of the Chinese space station was launched from the Wenchang Space Launch Site in Hainan, and entered the predetermined orbit accurately. The mission was a success. Subsequently, the Shenzhou 12th and 13th manned spacecraft were successfully launched on June 17 and October 16 respectively and achieved the rendezvous and radial rendezvous and docking between the manned spacecraft and the Tianhe core module.
3. Synthesis from carbon dioxide to starch
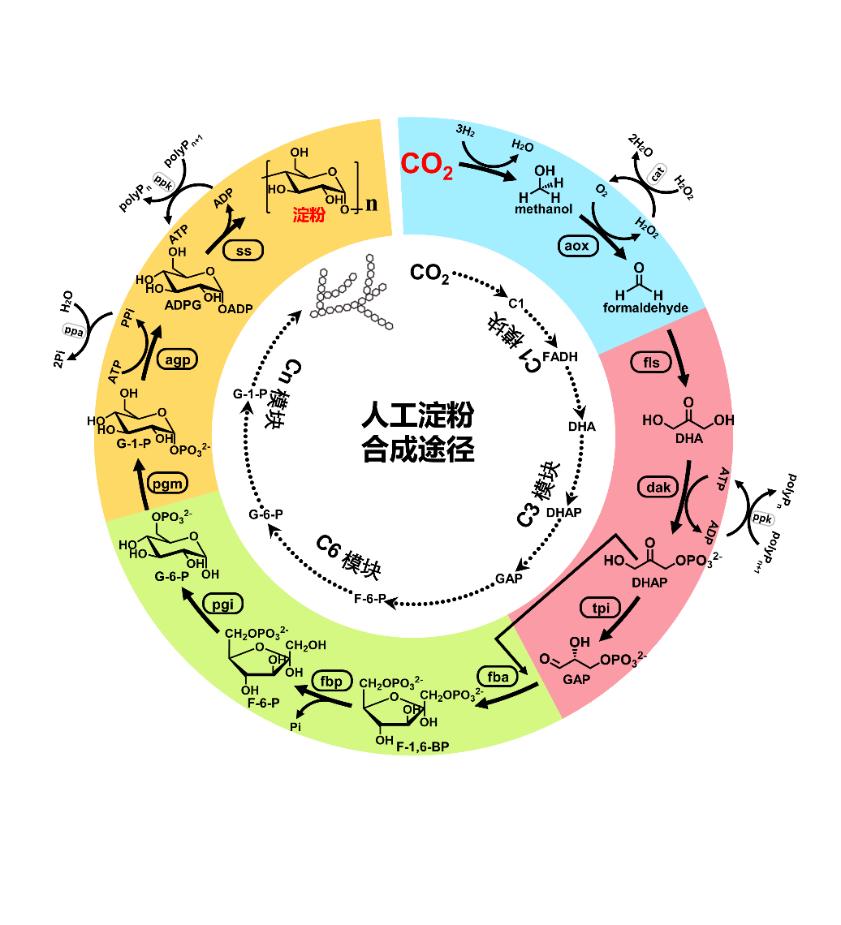
The artificial total synthesis of starch molecules from carbon dioxide and hydrogen was realized by Ma Yanhe, Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. This achievement does not rely on plant photosynthesis, which marks a major breakthrough in the field of artificial starch synthesis by humans, and is of great significance to many fields such as food security and industrial production.
4. Chang’e-5 lunar samples reveal the mystery of lunar evolution
Li Xianhua, Yang Wei, Hu Sen, Lin Yangting, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Li Chunlai, National Astronomical Observatory of Chinese Academy of Sciences, etc. used ultra-high spatial resolution dating and isotopic analysis techniques to study the basalt of the Chang’e-5 lunar sample. It is confirmed that the volcanic activity of the moon can continue until 2 billion years ago, and it also provides a key anchor point for the dating of impact craters. The lunar exploration and research proposed a new direction.
5. Reveal the mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 escaping antiviral drugs
Researchers from Tsinghua University Lou and ShanghaiTech University have discovered and reconstructed the viral “capped intermediate complex”, “mRNA capped complex” and “mismatch correction complex”, and elucidated their working mechanisms to optimize targeting of aggregation Enzyme-based antiviral drugs provide key scientific evidence and make important contributions to overcoming the spread of the new coronavirus.
6.FAST captures the world’s largest sample of fast radio storms
Li Di and others of the National Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences successfully captured the extreme activity period of FRB 121102 using the “China Sky Eye” FAST, and found that the burst rate of FRB has a characteristic energy E0=4.8×1037 erg, and detected the double-peak structure of its energy spectrum, showing for the first time The complete energy spectrum of FRB was obtained, and the basic physical mechanism of FRB was revealed in depth.
7. Realize the large-scale preparation of high-performance fiber lithium-ion batteries
Peng Huisheng and Chen Peining of Fudan University discovered a unique hyperbolic cotangent function relationship between the internal resistance and length of fiber lithium-ion batteries. The fiber lithium-ion battery constructed under the guidance of this theory has excellent and stable electrochemical performance, and successfully solves the major challenges in the field of lithium-ion batteries.
8. Quantum walk of programmable two-dimensional 62-bit superconducting processor “Zu Chongzhi”
The University of Science and Technology of China Zhu Xiaobo, Pan Jianwei and others realized the expansion of the qubit structure from one-dimensional to two-dimensional by developing a three-dimensional lead technology compatible with planar technology, and built the “Zu Chongzhi” quantum computing prototype, and demonstrated high fidelity through this device. One- and two-particle continuous-time quantum walks.
This work is the first published achievement in the field of superconducting quantum computing with more than 60 bits in the world. It verifies the high-precision quantum control capability of noisy medium-scale qubit systems. Computational Superiority” laid the foundation.
9. Self-powered soft robot successfully challenged Mariana Trench
Li Tiefeng et al. of Zhejiang University revealed the internal mechanism of soft robot functional device failure and drive failure under extreme pressure conditions in the deep sea; proposed a method of dispersing and integrating hard devices into a soft matrix to achieve internal stress regulation; established a system structure of a 10,000-meter deep-sea soft robot Methods and driving theory.
The self-powered soft robot developed successfully challenged the Mariana Trench, realized 10,900 meters of subsea diving and drive, and achieved deep-sea navigation at 3,224 meters below the sea level of the South China Sea, which greatly reduced the weight and economic cost of the deep-sea robot, and promoted the soft robot. Applications in deep-sea engineering.
10. Reveal the causes of bird migration routes and key genes for long-distance migration
Zhan Xiangjiang and others from the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences spent 12 years, using satellite tracking data and genomic information, to establish a set of Arctic peregrine falcon migration research systems, and found that peregrine falcons mainly use five routes to cross the Eurasian continent.
The study also found that peregrine falcons with longer migration distances carry a dominant allele of ADCY8, which is associated with long-term memory formation, suggesting that long-term memory may be an important basis for long-distance migration in birds.
The research combined remote sensing satellite tracking, genomics, neurobiology and other research methods, and clarified the causes and genetic basis of bird migration routes through multidisciplinary integrated analysis methods.